What is household hazardous waste?
Hazardous waste is unwanted material or products that can cause illness or death to people, plants and animals.
Household hazardous waste can be found anywhere in your home; in the kitchen, bathroom or laundry room, and storage areas like the garden shed, garage, basement, and attic.
Many common household products contain hazardous chemicals. Once released, these chemicals are free to contaminate our body, home and the environment.
Once you’ve cleansed your home of these toxics, you can replace them with some of our healthy cleaning alternatives and safely dispose of HHW.
How to identify hazard symbols

Toxic/Poison
These items poison or damage living organisms: solvents, batteries, antifreeze, medications, pesticides, fertilizers, wood stains and preservatives, radiator coolants, compact fluorescent light bulbs, and any confirmed or suspected carcinogens.

Corrosive
These items eat away at surfaces, including the skin of humans or animals. Corrosive materials include bleach and household cleaners, rust removers, wax strippers, laundry stain removers, oven cleaners, drain cleaners, and automotive lead-acid batteries.

Flammable
These items burn easily and pose serious risk of igniting with minimal spark or heat. They include fuel oil, gasoline, motor oil, kerosene, camping fuel, paint thinners, lighter fluids, contact cement, oil-based paints, insect repellent, partially full aerosol containers, furniture cleaners, paint brush cleaners, and gasoline/oil mixtures.
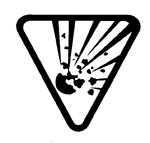
Reactive/Explosive
These pressurized containers contain materials that can poison or damage living organisms: gas cylinders that carry propane or butane and aerosol cans with unused product.
How to dispose of household hazardous waste
Correct disposal of household hazardous waste is important to prevent the spread of chemicals in our soil, air and water. When HHW ends up in landfills, it can leech out and contaminate our soil and groundwater.
Proper disposal ensures waste workers are not exposed to the risk of inhaling toxic substances and reduces the chance of fires or explosions. Never pour or flush HHW substances down the drain where they will enter the sewage system. Chemicals can corrode plumbing and cause failure in septic systems before they make their way to our waterways and oceans.
Some examples of HHW are: acetone, ant/wasp spray, barbeque starters, antifreeze, car waxes and polishes, glues, hair colouring, aerosol hair spray, lye, nail polish remover, paint thinners, rechargeable batteries, shoe polish, spa and pool chemicals, weed killers and windshield washer solution.
Some examples of household cleaners considered to be HHW are: abrasive cleaners, aerosol air fresheners, all-purpose cleaners, ammonia, bleach, disinfectants, drain cleaners, fabric softeners, glass cleaners, laundry starch, laundry stain removers, mildew removers, oven cleaners, rug and upholstery cleaners, toilet cleaners, and tub and tile cleaners.
Check with your province
Each Canadian province has instituted a household hazardous waste collection program to make it easy for Canadians to dispose of these toxic items with minimal environmental impact.
Before locating a depot near you:
- Keep materials in their original containers, or ensure that the containers are well labelled
- Do not mix different products together
- Tightly cap all containers



